Technological innovations are transforming healthcare in Europe, with advancements such as smart hospitals, AI in diagnostics, telemedicine, EHRs, robotic surgery, blockchain, VR/AR in training, 5G connectivity, health apps, wearables, and cybersecurity. These developments enhance patient care, streamline operations, and empower individuals in managing their health, promising a healthier future for European healthcare.
The healthcare sector in Europe is experiencing a significant overhaul, propelled by swift advancements in technology. The landscape is being reshaped by state-of-the-art medical devices and advanced data analytics, fundamentally altering the operational dynamics and care delivery methods of hospitals throughout the continent. This article will explore the most recent technological breakthroughs and their extensive influence on healthcare management across Europe.
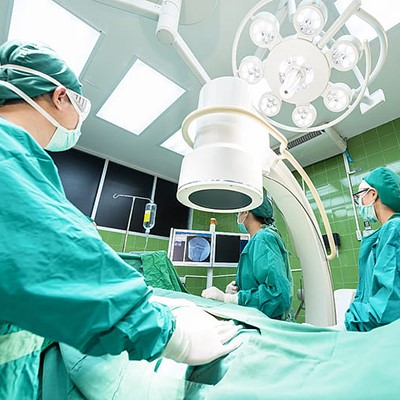
In Europe, the advent of smart hospitals is transforming patient care through strategic implementations of IoT devices and sensors. The integration of the Internet of Things within healthcare institutions is yielding significant advancements in patient monitoring, the automation of routine tasks, and an overall enhancement of operational efficiency. Wearable sensors and intelligent medical devices enable real-time monitoring, providing healthcare professionals with precise and timely patient data. The automation of tasks like inventory management and appointment scheduling not only streamlines hospital operations but also allows staff to dedicate more time to patient care. The seamless integration of IoT data with Electronic Health Records (EHRs) ensures a comprehensive and easily accessible flow of patient information across various departments. As smart hospitals in Europe continue to innovate, this technological convergence holds the promise of establishing a more patient-centric, data-driven, and efficient healthcare ecosystem.
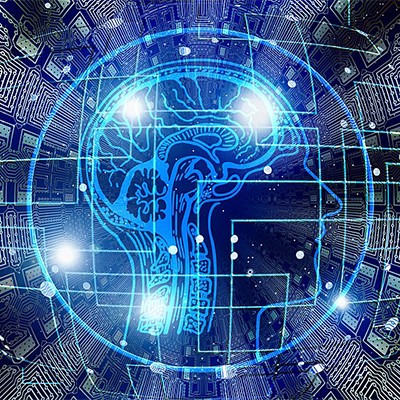

The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms has emerged as a transformative force in healthcare, particularly in the realms of diagnostics and treatment planning. In the diagnostic process, AI technologies are playing a pivotal role in assisting healthcare professionals by offering accurate and timely insights. AI-powered diagnostic tools, utilizing machine learning and deep learning algorithms, analyze complex medical data, such as imaging and pathology reports, with unparalleled precision. This not only expedites the diagnostic timeline but also enhances the overall accuracy of results.
Moreover, the influence of AI extends into personalized treatment planning, ushering in an era of tailored healthcare interventions. By leveraging patient-specific data, AI algorithms can analyze genetic information, medical histories, and treatment responses to recommend personalized treatment strategies. This level of precision enables healthcare professionals to move beyond a one-size-fits-all approach, optimizing therapeutic outcomes and minimizing potential side effects.
The evolving integration of AI into diagnostic and treatment workflows has the potential to revolutionize healthcare decision-making. The collaboration between human expertise and AI capabilities not only accelerates the diagnostic process but also heralds a new era of patient-centric treatment, representing a substantial advancement in healthcare service delivery.

The adoption of telemedicine platforms in European hospitals is rapidly reshaping the landscape of healthcare delivery, offering a paradigm shift toward remote consultations and real-time patient monitoring. This transformative technology has gained traction for its ability to bridge geographical gaps, improve accessibility, and enhance overall patient care.
Telemedicine offers a crucial advantage through remote consultations, enabling patients to engage with healthcare professionals from the convenience of their homes. This eliminates the requirement for physical travel and ensures prompt access to medical advice, especially beneficial for individuals in rural or underserved areas. The ability for real-time monitoring expands the scope of healthcare, allowing the continuous tracking of vital signs and chronic conditions. This proactive strategy improves the early detection of potential issues, facilitating timely interventions.
While telemedicine offers numerous benefits, its extensive implementation faces challenges. Concerns about the privacy and security of patient data during transmission, adherence to regulatory standards, and the necessity for standardized protocols present substantial obstacles. Additionally, achieving fair access to telemedicine services across varied populations is a persistent challenge that healthcare providers and policymakers must confront.
As European hospitals adopt telemedicine, it's crucial to address these challenges while capitalizing on the advantages of the technology. The incorporation of telemedicine platforms is promoting a healthcare model that is more patient-centric and flexible, showcasing the potential to transform the delivery and receipt of healthcare services throughout the continent.

The implementation of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) in European hospitals marks a pivotal shift towards digitization, significantly enhancing the efficiency and quality of healthcare delivery. These digital records play a crucial role in streamlining healthcare data management, offering a comprehensive solution to the challenges posed by traditional paper-based systems.
One of the primary advantages of EHRs is the improvement in data accessibility. With patient information stored in a digital format, healthcare providers gain instant access to critical medical histories, test results, and treatment plans. This not only expedites decision-making processes but also ensures that relevant information is readily available, contributing to more informed and personalized patient care.
Promoting collaboration among healthcare providers stands out as another significant advantage of EHR systems. Digital records facilitate the smooth sharing of patient information across various departments and healthcare facilities. This collaborative approach improves communication among medical professionals, fostering a comprehensive view of patient health and lowering the risk of errors or redundant tests. Interlinked EHR systems additionally enhance the efficiency of the referral system, especially in intricate cases that demand multidisciplinary care.
Additionally, the incorporation of EHRs significantly influences patient outcomes. Quick access to precise and current information expedites diagnosis and treatment decisions. EHRs also contribute to the advancement of preventive care initiatives by offering a comprehensive overview of a patient's health, empowering healthcare providers to proactively identify and address potential health risks.
While the transition to EHRs brings about numerous advantages, challenges such as data security, interoperability issues, and the need for staff training must be addressed. European hospitals are navigating these challenges to unlock the full potential of digital records in improving healthcare delivery.
The adoption of EHRs in European hospitals represents a transformative leap toward efficient and patient-centered healthcare. By leveraging digital records, hospitals are not only streamlining data management but also laying the foundation for a more interconnected, collaborative, and data-driven future in healthcare delivery across the continent.
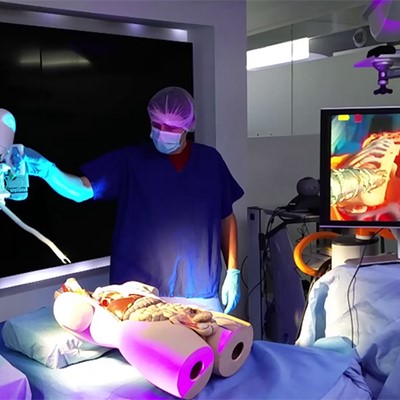
The incorporation of robotic-assisted surgery in European hospitals is reshaping the landscape of surgical procedures, introducing a new era marked by precision, efficiency, and improved patient outcomes. These robotic systems, designed to complement the skills of experienced surgeons, are making significant contributions across various surgical disciplines, spanning from minimally invasive procedures to complex interventions.
A primary benefit of robotic-assisted surgery is its capacity to elevate precision. The robotic arms, guided by the surgeon's exact movements, provide unparalleled accuracy when navigating within the constrained spaces of the human body. This precision results in diminished trauma to surrounding tissues, minimized blood loss, and heightened success rates for complex surgical procedures.
Robotic surgery offers the advantage of shorter recovery times as well. The minimally invasive nature of numerous robotic procedures results in smaller incisions, thereby decreasing postoperative pain and expediting recovery for patients. This not only boosts patient satisfaction but also improves the overall efficiency of healthcare delivery by reducing hospital stays and rehabilitation periods.
Improved surgical outcomes are a hallmark of robotic-assisted surgery in European hospitals. The three-dimensional visualization provided by robotic systems allows surgeons to navigate complex anatomical structures with enhanced clarity. This, coupled with the steady and controlled movements of robotic instruments, contributes to better surgical precision, particularly in delicate and intricate procedures.
Despite these advantages, the adoption of robotic surgery poses challenges, including the initial investment costs, the need for specialized training, and ongoing maintenance expenses. European hospitals are navigating these challenges to ensure the widespread availability of this cutting-edge technology and to maximize its potential in diverse surgical specialties.
The use of robotics in surgery represents a transformative leap forward in European healthcare. By embracing robotic-assisted procedures, hospitals are delivering precision and efficiency in surgical interventions, ultimately translating into improved patient outcomes and a paradigm shift in the way surgeries are approached and executed across the continent.
The integration of blockchain technology in European hospitals marks a significant advancement in securing healthcare data, safeguarding patient privacy, and enhancing the overall integrity of medical records. Blockchain, originally developed for secure financial transactions, has found a natural fit in the healthcare sector, where data security and privacy are paramount.
Blockchain plays a vital role in healthcare by ensuring data security. Its decentralized and cryptographic features offer a robust defense against unauthorized access and cyber threats, in contrast to traditional centralized databases that are prone to breaches. Patient data stored on a blockchain is encrypted and dispersed across a network of nodes, providing inherent resistance to tampering or unauthorized alterations.
Ensuring patient privacy is a paramount concern in healthcare, and blockchain technology excels in addressing this issue. It empowers patients with greater control over their health data by furnishing cryptographic keys for selective access and sharing of specific information. This decentralized control mitigates the risk of data misuse, while simultaneously enabling patients to securely contribute to research initiatives or share their records with healthcare providers.
Moreover, blockchain improves the integrity of medical records by establishing an immutable and transparent ledger of transactions. Each entry, including diagnoses, treatments, or test results, is time-stamped and interconnected with prior entries, forming an unalterable and chronological chain of information. This not only safeguards against data tampering but also guarantees a dependable and auditable trail of healthcare events, proving essential for medical research, audits, and legal purposes.
Despite its promise, the widespread adoption of blockchain in European healthcare faces challenges such as scalability, regulatory compliance, and interoperability with existing systems. However, ongoing efforts and collaborations within the healthcare industry aim to address these challenges, paving the way for broader implementation.
The application of blockchain technology in European hospitals represents a pivotal step toward fortifying data security, preserving patient privacy, and ensuring the integrity of medical records. As the healthcare sector increasingly recognizes the potential of blockchain, it holds the promise of reshaping the foundations of healthcare data management, instilling trust, and fostering a more secure and patient-centric healthcare ecosystem.
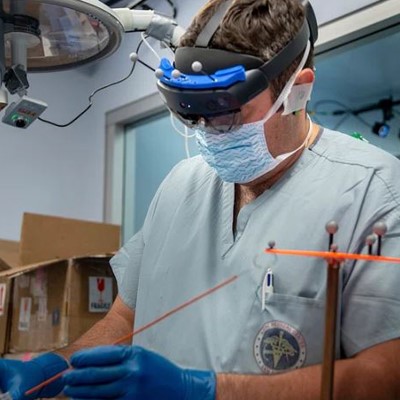
The integration of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies in healthcare training programs is catalyzing a transformative shift, providing medical professionals with immersive and realistic simulations to enhance their skills and expertise. These cutting-edge technologies are revolutionizing the traditional methods of training by offering dynamic, hands-on experiences that bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
VR in healthcare training creates immersive environments that replicate real-world scenarios, allowing medical professionals to practice procedures, surgeries, and critical decision-making in a risk-free and controlled setting. Surgeons, for example, can use VR to hone their skills by performing virtual surgeries before entering the operating room, contributing to increased precision and confidence during actual procedures.
On the other hand, AR supplements real-world environments with digital overlays, enhancing the learning experience by providing contextual information during training. This is particularly valuable in fields like anatomy, where medical students can visualize and interact with three-dimensional holographic representations of the human body, gaining a deeper understanding of complex structures and functions.
These technologies not only improve technical proficiency but also contribute to better collaborative and communication skills among healthcare professionals. VR and AR simulations often involve teamwork, enabling practitioners to practice coordination and communication in a realistic and dynamic environment, preparing them for the complexities of real-world healthcare scenarios.
The advantages go beyond the initial training phase. VR and AR applications make continuous learning and skill maintenance more engaging, enabling professionals to stay abreast of the latest medical advancements and refine their techniques throughout their careers.
While the adoption of VR and AR in healthcare training is gaining momentum, challenges such as cost, accessibility, and standardization need to be addressed for widespread implementation. Nevertheless, the ongoing development and refinement of these technologies promise to revolutionize how medical professionals are trained, fostering a new era of proficiency, confidence, and adaptability in the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare.

The rise of 5G technology is initiating a new era of connectivity in European healthcare, fundamentally shaping how medical services are delivered and accessed. With its focus on ultra-fast and reliable data transfer, 5G is catalyzing innovation in remote consultations, real-time data exchange, and the integration of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT).
One of the primary benefits of 5G in healthcare is its capacity to facilitate remote consultations with unprecedented speed and quality. The high bandwidth and low latency of 5G networks enable seamless video conferencing, providing a lifelike and interactive platform for patients to connect with healthcare professionals. This is particularly crucial in remote or underserved areas, where access to specialized medical expertise can be limited.
Real-time data transfer is another area where 5G is making a profound impact. In healthcare, timely access to patient data, medical records, and diagnostic information is critical for informed decision-making. The high-speed capabilities of 5G ensure that healthcare professionals can retrieve and exchange data in real-time, leading to quicker diagnoses, treatment decisions, and improved patient outcomes.
The integration of 5G also plays a central role in the advancement of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT). Connected medical devices, wearables, and sensors generate vast amounts of health-related data. With 5G, the IoMT ecosystem can thrive, enabling these devices to communicate seamlessly and transmit data instantly. This not only enhances the monitoring of patient's health but also contributes to preventive care and early intervention strategies.
While the potential benefits are immense, the deployment of 5G in healthcare is not without challenges. Security concerns, infrastructure development, and regulatory considerations are factors that must be addressed to ensure the reliable and secure implementation of 5G technology in healthcare settings.
5G connectivity is reshaping the landscape of European healthcare by providing the foundation for high-speed, low-latency communication. The transformative impact of 5G is evident in its ability to enhance remote consultations, facilitate real-time data transfer, and propel the growth of the Internet of Medical Things, ultimately contributing to a more connected, efficient, and patient-centric healthcare ecosystem across Europe.
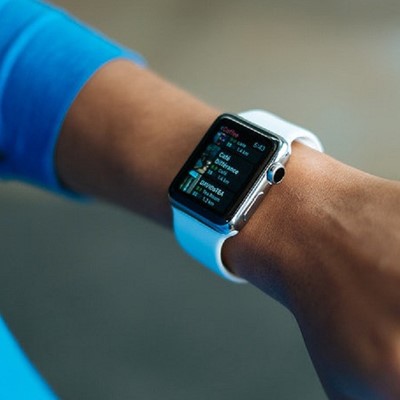

The widespread adoption of health apps and wearables has inaugurated a new era of patient empowerment. These tools offer individuals the means to actively oversee their health, monitor vital signs, and participate in preventive care initiatives. This synergistic integration of technology and healthcare is redefining the conventional patient role, encouraging active participation, and instilling a sense of responsibility for one's well-being.
Available on smartphones and other devices, health apps provide users with a broad range of functionalities to track different aspects of their health. From monitoring physical activity and sleep patterns to logging dietary choices, these apps offer real-time insights into lifestyle choices and habits. Additionally, many apps present personalized recommendations and reminders, motivating users to adopt healthier behaviors and adhere to medical prescriptions.
Wearables, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, represent a tangible extension of health apps, offering continuous monitoring of vital signs and activity levels. These devices track metrics like heart rate, steps taken, and even sleep quality, providing users with a comprehensive overview of their physical well-being. The real-time nature of wearable data enables individuals to make informed decisions about their health on a day-to-day basis.
Engaging in preventive care initiatives is a fundamental element of patient empowerment facilitated by health apps and wearables. Users can establish health goals, receive alerts for vaccinations or screenings, and actively participate in wellness programs. This transition towards prevention plays a pivotal role in alleviating the burden on healthcare systems and fostering a culture of proactive health management.
Despite the numerous benefits, challenges such as data privacy, accuracy of measurements, and the need for healthcare professional integration remain important considerations. As the adoption of health apps and wearables continues to rise, collaborations between tech developers, healthcare providers, and regulatory bodies are crucial to ensuring the reliability and security of these technologies.
The integration of health apps and wearables is reshaping the patient experience, placing individuals at the center of their healthcare journey. By actively monitoring and managing their health, patients are not only empowered to make informed decisions but also contribute to a broader shift towards a preventive and patient-centric healthcare paradigm.

In the digital age of healthcare, the increasing reliance on electronic systems and data-driven technologies necessitates a heightened focus on robust cybersecurity measures. European hospitals, as custodians of vast amounts of sensitive patient information, are recognizing the paramount importance of implementing and continually improving cybersecurity measures to protect patient data, ensure system integrity, and fortify defenses against evolving cyber threats.
The proliferation of electronic health records (EHRs), interconnected medical devices, and telehealth platforms has exponentially increased the volume of sensitive health data stored and transmitted within healthcare systems. Consequently, the need for stringent cybersecurity protocols has become more critical than ever to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential exploitation by malicious actors.
Patient data, including personal information, medical histories, and treatment plans, represents a prime target for cybercriminals. Robust encryption, access controls, and secure authentication mechanisms are integral components of cybersecurity strategies in European hospitals to ensure the confidentiality and privacy of patient information. Regular audits and assessments help identify vulnerabilities and strengthen defenses against potential breaches.
Maintaining the integrity of healthcare systems is equally vital. Unauthorized alterations to medical records or interference with treatment plans can have severe consequences for patient safety. European hospitals are increasingly implementing measures such as blockchain technology, which provides an immutable and transparent record of transactions, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of medical data.
The threat landscape in cybersecurity is dynamic, with cyber threats evolving in sophistication and frequency. Hospitals in Europe are investing in advanced threat detection and response mechanisms, leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning to identify anomalous activities and potential security breaches in real-time. Regular staff training and awareness programs also play a crucial role in preventing common security pitfalls, such as phishing attacks.
Collaboration within the healthcare industry, information sharing about emerging threats, and adherence to international cybersecurity standards are essential elements of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. European hospitals are actively participating in these collaborative efforts to strengthen the collective resilience against cyber threats.
The growing emphasis on robust cybersecurity measures in European hospitals underscores a dedication to protecting sensitive patient data, maintaining the integrity of healthcare systems, and strengthening defenses against evolving cyber threats. As the digital transformation of healthcare advances, continuous investments in cybersecurity will be essential to preserve trust, safeguard patient privacy, and uphold the high standards of care for which European hospitals are renowned.
As European hospitals embrace these technological innovations, the future of healthcare management looks promising. From improved patient outcomes to streamlined operations, the transformative power of technology is reshaping the way healthcare is delivered and managed across the continent. Stay tuned for continued advancements as Europe leads the way in leveraging technology to build a healthier future.